Describe How Antibodies and Antigens Work
Most COVID-19 vaccines just like natural infections produce substantial antibodies in people who have received them. The antibody has the function of eliminating the antigens.
Best Immune System Booster Tea Immune System Attacks Spinal Cord Do Energy Drinks Weaken Your Immune System.
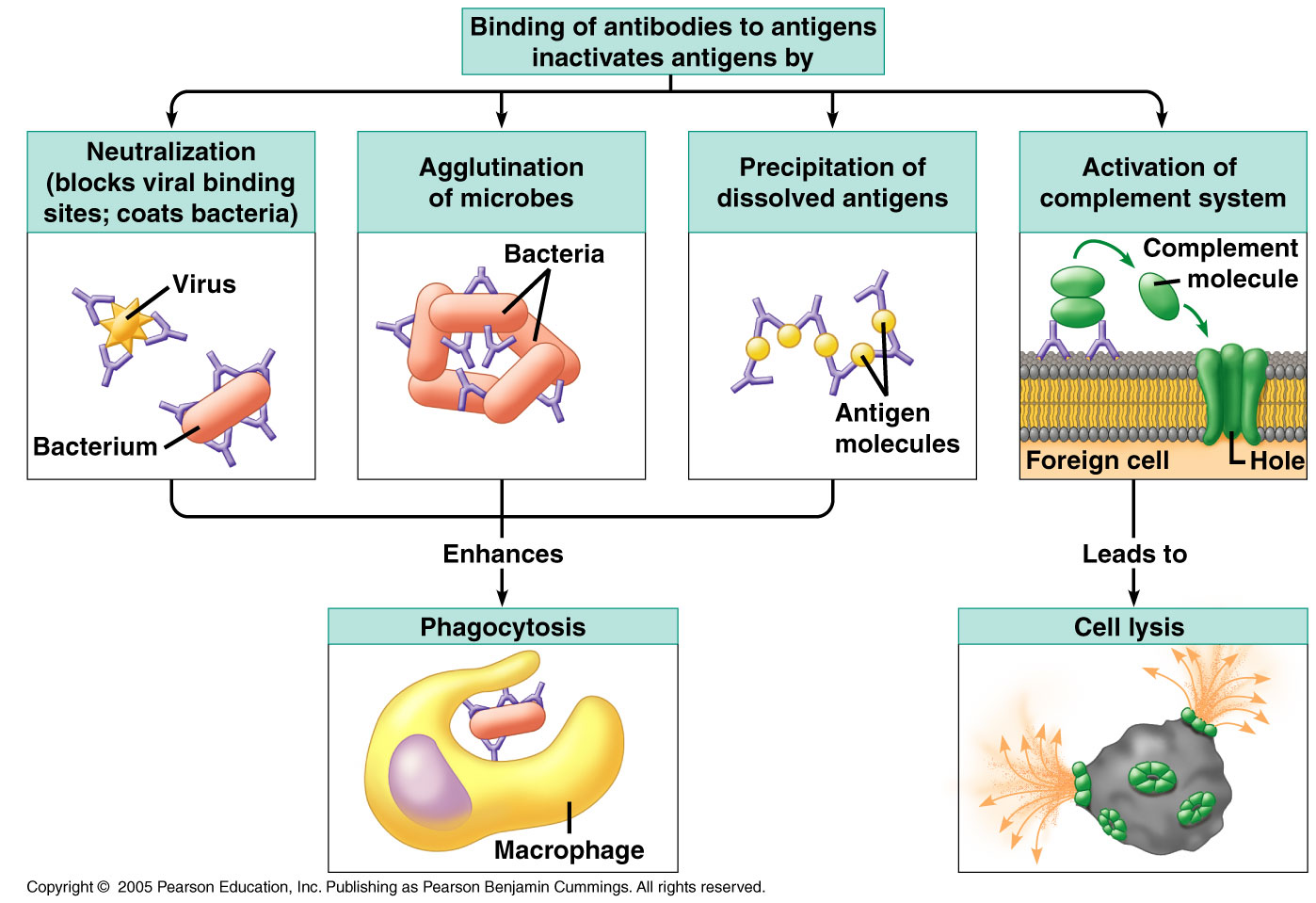
. Describe how antibodies and antigens work related to blood transfusions. The antibodies destroy the antigen pathogen which is then engulfed and digested by macrophages. Antigen-antibody interaction or antigen-antibody reaction is a specific chemical interaction between antibodies produced by B cells of the white blood cells and antigens during immune reaction.
Type O- no antigens AB antibodies. Each subunit has two identical light and heavy chains. Antibodies help the immune system fight infections by latching onto antigens and marking them for destruction.
The type of antigen on ones red blood cells determines ones A-B-O blood type. List the major antigens and common phenotypes. They fight off the foreign invaders called Antigens to protect our body.
For each of the blood group systems described in this chapter. The reaction between the antigen and the antibody follows the key-lock model due to its specificity. Self-antigens like cancer cells form within the body.
Our bodies have specialised Warriors named Antibodies. Antigens may not be the main attraction when it comes to immunity but they play a crucial role in the prevention and elimination of diseases. This acts as a flag for other immune cells that can produce chemicals that kill the unwanted target cell.
Type A- A antigens anti- B antibodies. These dormant antigens cause your B cells to produce specific antibodies to combat the illness. When an antigen enters the body the immune system produces antibodies against it.
When the body recognises a foreign antigen lymphocytes white blood cells produce antibodies which are complementary in shape to the antigen. Type B- B antigens anti-B antibodies. Molecular recognition of aggressive agents.
Antigen-antibody reactions are a mainstay for the rapid detection of proteins. An antibody will only work on one type of. Describe the serologic characteristics.
Phagocytosis This is quite similar to the previous mechanism. Antigens are mostly made up of proteins but they may also be nucleic acids carbohydrates or lipids. The antigen acts as an antibody generator and it gets eliminated along with the infectious agent by the bodys immune system.
People with type A blood have A antigens on their red blood cells those with type B blood have B antigens and those with type O blood have no antigens on their red blood cells. Vaccines increase the number of antibodies against a particular antigen in your body. The immune system responds to the antigen by producing a substance called an antibody which is specific to that antigen.
Antibodies are always Y-shaped. The N-terminus of each heavy chain forms an antigen-binding domain with a light chain. Each antibody has a unique binding site shape which locks onto the specific shape of the antigen.
Cells that create clots to stop bleeding. Describe How Antibodies And Antigens Interact In The Immune System Is The Zika Virus Evading Innate Immune System Non Specific Innate Immune System And Includes Brain Tumor And Immune System. There are two antigen-binding domains forming the.
The antigens and antibodies combine by a process called agglutination. O- can give to all A- can give to AB. Is the bonding of antigen - Answered by a verified Tutor We use cookies to give you the best possible experience on our website.
Blood that has antigensantibodies on it that isnt recognized by the body will be attached by your immune system. An antibody has a Y-shaped structure made up of four polypeptide subunits. Antigen and Antibody.
Describe how antibodies and. Every red blood cell contains either an A antigen a B antigen or no antigen this is called type O. List the four categories for classification of RBC surface blood group antigens used by the ISBT.
What factors determine the strength of this bond. Antigens are typically divided into self and non-self-antigens. Different Types and Their Functions.
Type AB- AB antigens no antibodies. Only in this case the antibody bound to an antigen recruits phagocytes. Describe how antigens antibodies genes and phenotypes are correctly written.
Antibodies - An antibody is a specialized substance produced by the body that can provide immunity against a specific antigen. - Activated B-cells or their plasma offspring are. Antibodies help the immune system fight infections by latching onto antigens and marking them for destruction.
They are formed in response to a huge number of different antigens. Nowadays instead of employing essential antigen components vaccinations use genetic blueprints for creating antigens which work similarly. What blood type can give to what blood type.
Up to 25 cash back Describe how antigens and antibodies bond. The antibody binds to the antigen on an intruder or an abnormal infected cell the pink cell in the image. Want to know more about these.
Non-self-antigens come from outside the body. List and describe the 4 blood types.



No comments for "Describe How Antibodies and Antigens Work"
Post a Comment